Night Eating Syndrome (NES) is a complex eating disorder that involves a specific pattern of food consumption during late-night hours, often connected to various emotional and physical triggers.
As awareness of this condition continues to grow, it becomes increasingly important to understand its prevalence, its effects on health, and effective management strategies.
This article delves into the various dimensions of NES, including how to identify its triggers, discover coping mechanisms, and explore professional support options.
We invite you to join us on this journey toward healthier habits and a more positive mindset regarding nighttime eating.
Understanding Night Eating Syndrome
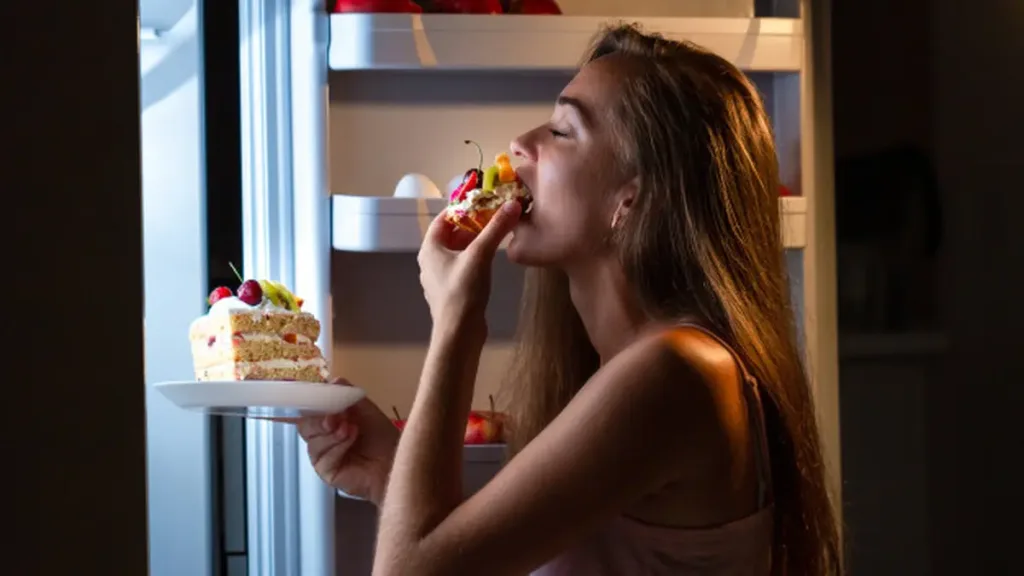

Night Eating Syndrome (NES) is a complex eating disorder marked by the tendency to consume large amounts of food, primarily during late-night hours. This condition can interfere with sleep patterns and lead to serious health issues, affecting both emotional well-being and overall appetite control.
People experiencing NES may grapple with intense food cravings at night, which are often tied to a range of psychological factors and lifestyle choices that promote emotional eating. Gaining a deeper understanding of NES is essential for creating effective solutions and strategies aimed at weight management and enhancing overall health.
Definition and Prevalence
Night Eating Syndrome is a condition characterized by individuals consuming a substantial portion of their daily caloric intake during the night, often linked with insomnia or sleep deprivation.
This distinctive eating pattern usually presents specific symptoms, including a lack of appetite in the morning, heightened cravings for high-calorie or carbohydrate-rich foods at night, and feelings of guilt or shame tied to nighttime eating. Unlike binge eating disorder, which is marked by episodes of losing control over eating at any time of the day, Night Eating Syndrome is specifically associated with nighttime consumption and often affects individuals who do not maintain regular eating habits during the day.
Research suggests that approximately 1-3% of the general population may experience this syndrome, with a higher prevalence noted among individuals with obesity and those undergoing treatment for conditions such as depression or anxiety. Understanding these nuances is essential for developing effective interventions and providing appropriate support for those impacted.
Further reading: How to Manage Nausea When Hungry: Symptoms and Solutions
Triggers for Night Eating
Understanding the triggers for Night Eating Syndrome is crucial for effectively addressing this eating disorder. Both emotional and physical factors can significantly influence late-night snacking behaviors, making it important to consider these aspects in any treatment approach.
Emotional and Physical Triggers
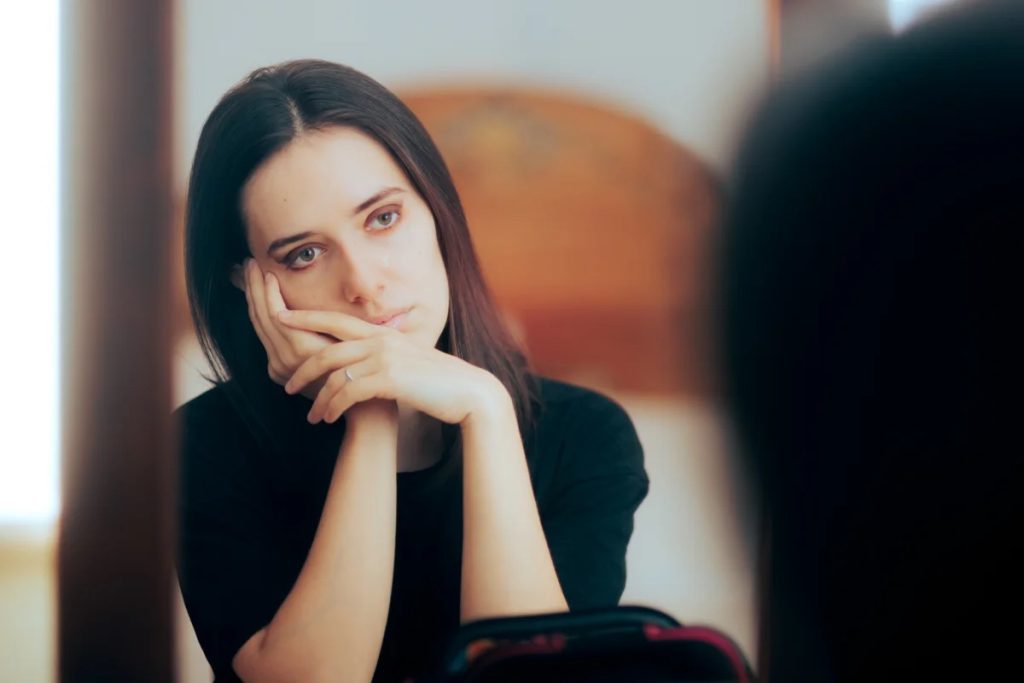

Emotional triggers such as stress, anxiety, and depression can significantly impact eating behaviors, often resulting in binge eating or late-night snacking as a way to cope. These emotions can create a scenario where food becomes a source of comfort, offering temporary relief from intense feelings.
Additionally, hormonal fluctuations and disrupted sleep patterns can intensify cravings, particularly for sugary and high-calorie foods. Psychological factors, including low self-esteem and challenges with emotional regulation, further complicate the relationship with food. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to cultivate emotional resilience.
Employing strategies such as mindfulness meditation, maintaining a food journal, and seeking professional support can be beneficial. These approaches not only assist in identifying specific triggers but also give the power to individuals to respond to them with healthier coping mechanisms, ultimately promoting a more balanced relationship with eating.
Effects of Night Eating Syndrome
The effects of Night Eating Syndrome can be significant, influencing not just a person’s physical health but also their emotional well-being and overall quality of life. It’s important to recognize how this condition can interconnect with various aspects of an individual’s life.
Impact on Health and Well-being
Night Eating Syndrome poses various health risks, including obesity, sleep disorders, and adverse effects on psychological well-being. Therefore, it is essential to address this condition in a timely manner.
Individuals affected by this syndrome often face challenges with appetite regulation, leading to heightened cravings for high-calorie, sugary foods during late hours, which can exacerbate weight gain. These nighttime eating habits may also negatively impact sleep quality, creating a troubling cycle of fatigue and increased emotional distress. Along with these physical effects, the psychological impact can be quite significant, as individuals may experience feelings of guilt and shame following binge episodes.
To help alleviate these cravings and promote better overall health, implementing behavioral strategies can be beneficial. Mindful eating practices, identifying triggers for late-night cravings, and establishing a consistent sleep schedule are all effective approaches to managing this condition.
Further reading: How to Overcome Food Addiction: 5 Easy Tips to Follow
Strategies for Managing Night Eating
Developing effective strategies to manage Night Eating Syndrome requires the implementation of healthy habits and coping mechanisms that address the underlying triggers of nighttime food cravings. By focusing on these triggers, individuals can create a more balanced approach to their eating patterns and improve their overall well-being.
Healthy Alternatives and Coping Mechanisms
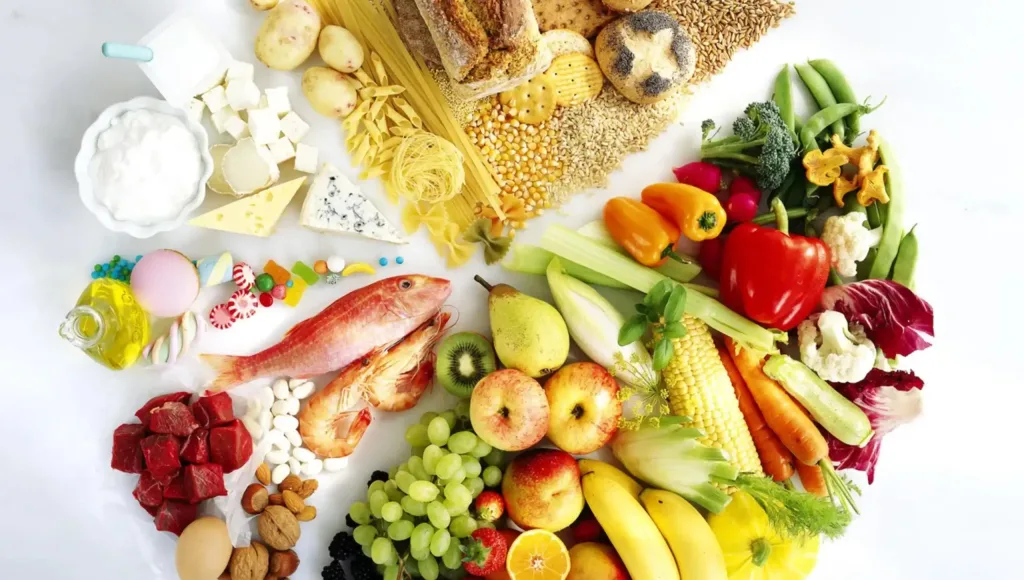

Incorporating healthy alternatives and effective coping mechanisms can greatly reduce the temptation for late-night snacking and support a balanced diet.
By opting for nutrient-dense choices like yogurt with fresh fruit, air-popped popcorn, or vegetables paired with hummus, individuals can satisfy their cravings without succumbing to unhealthy foods.
It is also crucial to understand the triggers for nighttime munchies. Engaging in a hobby or immersing oneself in a captivating book can effectively redirect attention away from food.
Establishing regular meal times throughout the day helps maintain consistent energy levels, which can minimize hunger pangs in the evening.
Furthermore, practicing portion control—such as using smaller bowls or pre-portioned snacks—can assist in fostering a balanced approach to nighttime eating habits.
Further reading: 25 Healthy Road Trip Snacks That Can Stay Fresh for Hours
Seeking Professional Help
When self-management strategies prove insufficient, seeking professional assistance for Night Eating Syndrome can offer individuals the essential support and guidance needed to navigate this challenging condition effectively.
Therapy and Support Options
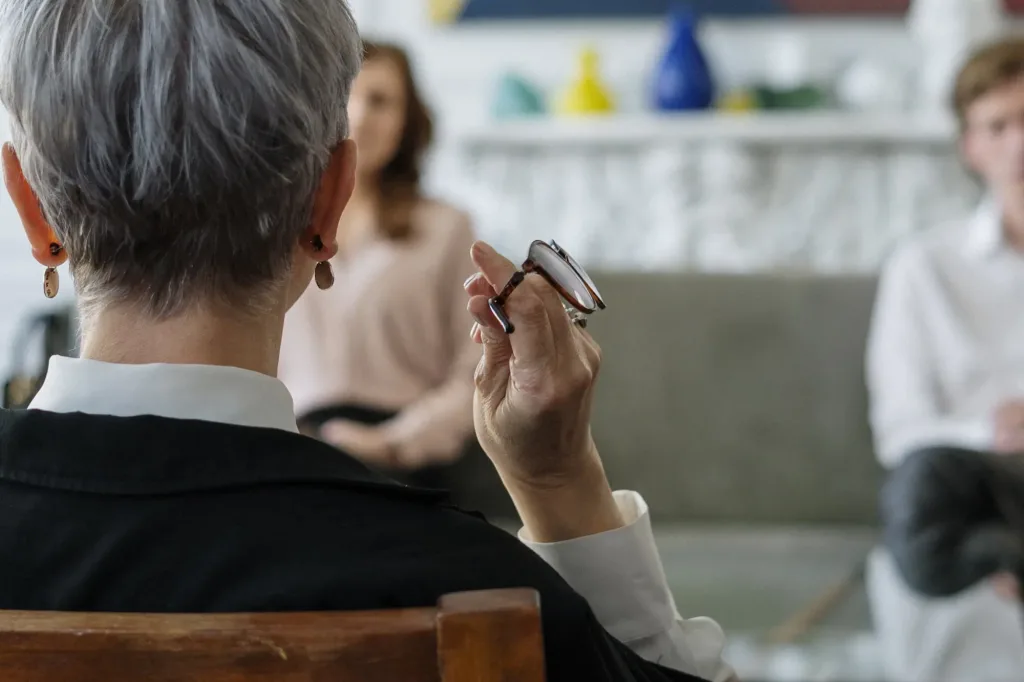

There are several therapy and support options available for individuals grappling with Night Eating Syndrome, such as psychotherapy, behavioral therapy, and nutritional therapy.
Support groups also play a vital role in creating a sense of community and shared experiences, which can be incredibly beneficial in the recovery process. Psychotherapy aims to identify the emotional triggers that contribute to the syndrome, helping withdividuals in developing effective coping strategies. On the other hand, behavioral therapy focuses on modifying unhelpful eating patterns using practical techniques and routines. Nutritional therapy offers personalized meal plans designed to restore balanced eating habits while addressing the nutritional deficiencies that often accompany this condition.
By integrating these approaches, individuals can navigate a holistic pathway toward healing, benefiting from both professional guidance and the support of their peers.
Preventing Relapse
Preventing relapse in Night Eating Syndrome involves a dedicated commitment to maintaining healthy habits and implementing lifestyle interventions that promote motivation and self-discipline.
It’s essential to create a supportive environment that encourages these positive changes and helps individuals stay focused on their goals.
Maintaining Healthy Habits and Mindset
Establishing and maintaining healthy habits is essential for individuals recovering from Night Eating Syndrome, as it significantly contributes to long-term emotional stability and nutritional balance.
Creating a supportive environment that prioritizes mindful practices can greatly enhance recovery efforts. This involves developing routines that encourage mindful eating, allowing individuals to fully savor their meals while being attentive to their hunger cues.
Meal planning also plays a crucial role in this process. It helps organize food choices to ensure they not only provide essential nutrients but also foster a sense of control and preparation. Addressing any nutritional deficiencies through balanced diets can lead to improved energy levels and better mood stability, ultimately enhancing overall well-being.
By integrating these strategies, individuals can build resilience and establish a healthier relationship with food, driving them toward sustained recovery and personal growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Night Eating Syndrome and what are its triggers?
Night Eating Syndrome (NES) is a disorder characterized by consuming a significant amount of food after dinner and during the night. The triggers for NES can vary, but often include stress, emotions, and irregular eating patterns.
How can stress contribute to Night Eating Syndrome?
Stress can lead to Night Eating Syndrome by causing an increase in the stress hormone cortisol, which can stimulate appetite and cravings for high-carbohydrate and high-fat foods.
Are there any specific emotions that can trigger Night Eating Syndrome?
Emotions such as anxiety, loneliness, boredom, and sadness can all contribute to night eating. These emotions may lead to seeking comfort in food during the night, even if you are not physically hungry.
What are some solutions for stopping Night Eating Syndrome?
To stop Night Eating Syndrome, it is important to address the underlying triggers and develop healthy coping mechanisms. This can include stress management techniques, seeking support from friends and family, and establishing a regular eating schedule.
Can certain medications contribute to Night Eating Syndrome?
Yes, some medications, such as antidepressants and sleep aids, can increase appetite and lead to night eating as a side effect. If you are experiencing NES and are taking medication, it may be helpful to discuss this with your doctor.